
One of the Only Centers in the World Offering Minimally Invasive Liver Surgery
The AdventHealth Digestive Health Institute is one of the first and only centers in the world to offer minimally invasive robotic surgery for liver resection, which helps patients experience easier, faster recoveries. The liver is an important digestive organ that has more than 500 known functions. It is the body’s only organ that can regenerate itself. Cancer that starts in the liver is known as primary liver cancer. Although there are several types of primary liver cancer, two are most common. Hepatocellular carcinoma is a cancer of the liver cells, and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma is a cancer of the bile ducts inside the liver.
Hepatocellular carcinoma is often caused by cirrhosis, which is scarring of the liver. Cirrhosis is often the result of liver disease. Liver disease can be caused by excess alcohol consumption, hepatitis B or C, or a buildup of fatty tissue in and around the liver. It is also quite common for other cancers to spread, or metastasize, to the liver, which is centrally located in the torso. Colon and rectal, pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors, soft tissue sarcomas, breast, stomach, esophageal, melanoma, ovarian and uterine cancers are most likely to spread to the liver.
Whole-Person Care for Liver Cancer
- Symptoms
- Diagnosis
- Treatment Surgery for Primary
- Treatment Surgery for Secondary
- Non-Surgical Treatment
Many of the symptoms of liver cancer can be very similar to symptoms of other liver and digestive conditions.
Liver cancer symptoms may include:
- An enlarged liver, as felt under the ribs on the right side
- An enlarged spleen, as felt under the ribs on the left side
- Loss of appetite and/or feeling full soon after eating
- Unintended weight loss
- Nausea and vomiting
- Abdominal pain, swelling or fluid buildup
- Pain near the right shoulder blade
- Jaundice, or yellowing of the skin and eyes
- Itching
If your doctor suspects that you could have liver cancer, you will receive some tests:
- Blood testing
- One or more imaging tests, which may include an ultrasound, CT scan and/or MRI scan
- A guided needle biopsy to remove tumor cells for biopsy if an imaging tests shows a suspicious liver mass
- The cell sample will be studied under a microscope by a pathologist to determine if they are cancerous or not.
- More imaging tests may be done if the sample shows cancer to make sure the liver cancer has not spread.
- A laparoscopic exploratory surgery is sometimes needed. This is a minimally invasive procedure that can help doctors see liver tumors better, collect tumor cells for biopsy and plan the best surgical approach for treatment.
Treatment options for any type of primary liver cancer depend on the location and size of the tumor as well as how much of the liver would be left if some of it had to be removed. Liver resection, or surgically removing part or all of the liver, is the standard treatment for most tumors. Because of the regenerative nature of the liver, almost all patients can tolerate major liver resection for cure.
Robotic Liver Resection
The AdventHealth Digestive Health Institute is one of the only places patients can find minimally invasive robotic surgery for liver resection. Minimally invasive surgery helps patients experience easier, faster recoveries. Robotic-assisted surgery is one of the latest, most innovative advancements in medicine, helping make more surgical procedures minimally invasive ones. invasive ones.
Patients benefit from robotic surgery in the following ways:
- Shorter hospital stay. Most patients can leave the hospital 2 to 3 days after a liver resection.
- Faster recovery. Having a robotic liver procedure instead of an open procedure results in a dramatically faster and easier recovery. Many patients report being able to return to their normal activities in 1 to 2 weeks instead of 6 to 12 weeks.
- Lower risk for complications. Not having a large, open incision lowers the chance that patients will experience heart or breathing problems after surgery. Having a minimally invasive liver resection also lowers the chances of developing an infection or a hernia.
- Less blood loss. Less blood is lost during a minimally invasive procedure, so there is less of a chance that patients will need blood transfusions during or after surgery.
- Less pain and scarring. In addition to being left with smaller, less noticeable scars, patients do not experience as much pain after surgery and require less pain medication.
- Faster return to cancer treatment. A fast recovery is especially important for patients with cancer. It means they can begin other portions of their cancer treatment, such as radiation therapy or chemotherapy, much sooner.
About 50 percent of patients diagnosed with colon or rectal cancers will have their cancer spread to the liver. It is common to discover cancer in the liver at the same time colorectal cancer is diagnosed. Many other cancers often spread, or metastasize, to the liver as well. For patients with other cancers that have metastasized to the liver, there are treatment options that can often cure the condition.
Treatments for secondary liver cancer include:
- Liver resection
- Liver ablation
- A combination of both
Before liver resection is considered for metastasized cancers, a series of tests will be done to make sure it is the right treatment approach. If liver resection is not right for the patient, other treatment options include any of the non-surgical treatments described above. Chemotherapy will also be part of treatment for cancer that has metastasized to the liver, either before or after other treatments.
For various reasons, liver surgery is not a an appropriate treatment option for every patient, but when resection is not aa there are other treatments for primary liver cancer tumors that can be used instead.
Liver Tumor Ablation
One approach is tumor ablation, which is ideal for small tumors. At the Digestive Health Institute, liver tumor ablation is done as a minimally invasive procedure through one very small incision in the belly button. A needle that creates heat through a high frequency is placed near the tumor. This heat destroys, or ablates, the cancer cells. Studies have shown that for small tumors, ablation is about 85 percent effective in preventing cancer from coming back.
Transarterial Treatments
Patients with larger liver tumors who cannot have surgical treatment may benefit from a transarterial approach. The liver specialists at DHI collaborate with interventional radiologists to offer these types of minimally invasive treatments. Transarterial treatment of liver tumors involves a thin, flexible tube called a catheter inserted through an artery in the inner thigh and fed up to the liver. Then, small beads laced either with chemotherapy or radiation are injected through the catheter and into the tumor. These beads shrink the tumor and reduce the chance that it will come back.
Surgical Cancer Care
-
Esophageal Cancer
Typically esophageal cancer requires surgery in addition to radiation and chemotherapy. Learn more about the surgical treatments our specialists can provide.
-
Gastric/Stomach Cancer
We help diagnose and treat stomach cancer. We even have minimally invasive options. Learn more about how our gastroenterologists can help you.
-
Duodenal/Small Bowel Cancer
Our gastroenterologists diagnose and treat small bowel and duodenal cancer. We offer three minimally invasive treatment options.
-
Pancreatic Cancer
Our surgeons are among the region’s most experienced in pancreatic surgery. We can help treat your cancer with minimally invasive options. Learn more today.
-
Liver Cancer
Our AdventHealth Digestive Health Institute surgeons offer surgical and non-surgical liver cancer treatments, depending on your specific case. Schedule an appointment with one of our gastroenterologists.
-
Gallbladder Cancer
Removing the gallbladder with cancer is a very complex surgery that requires highly experienced surgeons like those at AdventHealth Digestive Health Institute.
-
Colon and Rectal Cancer
Our experienced gastroenterologists can diagnose and treat colon and rectal cancer. Learn more about treatment and surgery options.
-
Anal Cancer
Our colon and rectal surgeons can help diagnose and treat anal cancer. We offer anal cancer surgery when necessary.
-
Public Reporting of Outcomes
Our compassionate medical staff is committed to providing high-quality healthcare services in Hillsborough County.
Amazing Success Story
After a colon test led to a diagnosis of stage 4 colon cancer, William turned to the experts at AdventHealth Digestive Health Institute for an innovative surgical procedure in which his colon and parts of his liver were resected in the same operation. Watch his story.
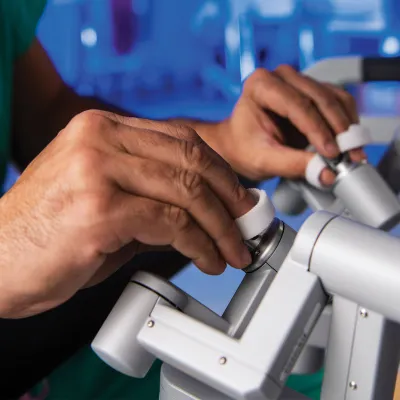
Recover Faster With Minimally Invasive and Robotic Surgery
The expert surgeons at the AdventHealth Digestive Health Institute have a large depth of experience in offering minimally invasive surgery.

Meet Your Dedicated Experts
Our specialists are passionate about providing collaborative care that addresses your unique needs and goals while ensuring you feel informed and supported every step of the way. Learn more about our team and their areas of expertise.

Surgical Consultations For Digestive Cancer Without the Wait
Appointments Within Seven Days for Patients with Cancer
At AdventHealth Digestive Health Institute, we know that after being diagnosed with cancer, patients want and often need to begin treatment quickly. So we make it a priority to offer appointments for cancer surgery consultations within five business days, and often earlier.
Patients who are newly diagnosed with cancer, or have just found out they have cancer again, qualify for this priority access. Our surgeons will make themselves available to see you right away, even for a second opinion. We want to help you start your treatment as soon as possible.
Let Us Help You Feel Whole Again
Whether you’re experiencing new symptoms or want a second opinion on a diagnosis, our dedicated digestive health experts are here to help you find answers and a path forward. Request an appointment today to take charge of your health and get the personal support you need.

